Compassionate nursing is at the heart of our approach, offering health…
페이지 정보

본문
Compassionate care is at the heart of effective nursing practice, shaping how healthcare professionals deliver treatment, connect with patients, and improve outcomes. For nurses, developing essential nursing skills and fostering healthcare compassion is critical to patient care and overall well-being. At NurseSkillsHub.com, our mission is to provide comprehensive resources that empower nurses to elevate their careers while enriching the lives of those they serve.
The Role of Compassionate Care in Nursing
Compassionate nursing goes beyond clinical expertise. It involves empathy, active listening, and genuine concern for patients’ physical, emotional, and mental well-being. This approach is especially vital in creating trust, ensuring adherence to treatment plans, and improving patient satisfaction.
Key Benefits of Compassionate Care:
Improved Patient Outcomes: Empathy and kindness encourage cooperation, leading to faster recoveries.
Stronger Nurse Skills Hub-Patient Relationships: Building trust fosters open communication and enhances care delivery.
Increased Patient Satisfaction: Compassion helps patients feel valued, reducing anxiety and stress.
Positive Workplace Culture: A focus on empathy benefits not only patients but also healthcare teams.
Essential Nursing Skills for Quality Patient Care
Quality patient care relies on advanced nursing skills and consistent professional development. Nurses must blend technical expertise with emotional intelligence to provide well-rounded care. The following skills are vital for success:
Clinical Nursing Skills:
Effective Nursing Communication: Ensures clarity in patient interactions and fosters understanding.
Nursing Care Techniques: Includes wound care, IV administration, and pain management in nursing.
Patient Advocacy: Protecting patient rights and ensuring ethical care delivery.
Advanced Care Planning: Helps patients make informed decisions about their healthcare.
Compassionate Nursing Techniques:
Active Listening: Understanding patient concerns and responding empathetically.
Emotional Support for Patients: Addressing fears and offering reassurance during critical moments.
Personalized Care Plans: Tailoring treatments to individual needs, especially for the elderly or chronically ill.
Nursing Education: Building a Foundation for Excellence
Education is the cornerstone of professional nursing development. Continuous learning equips nurses with the tools they need to adapt to evolving healthcare challenges.
Key Areas of Nursing Education:
Nursing Certifications: Programs like Basic Life Support (BLS) and Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support (ACLS) build critical care skills.
Nursing Training Programs: Hands-on training sharpens both technical and soft skills.
Clinical Nursing Education: Enhances decision-making through evidence-based practices.
Healthcare Leadership for Nurses: Prepares professionals for management roles and fosters teamwork.
Patient-Centered Care: Prioritizing Individual Needs
Patient-centered care places the individual at the core of healthcare delivery. This holistic approach ensures that treatment aligns with patient values, preferences, and circumstances.
Strategies for Patient-Centered Nursing:
Care Coordination Skills: Collaborate across teams to provide seamless care.
Cultural Competency: Respect diverse backgrounds and tailor care accordingly.
Patient Advocacy: Champion patient rights while navigating healthcare systems.
Holistic Nursing Care: Address physical, emotional, and psychological needs.
Nursing Leadership: Driving Change in Healthcare
Effective nursing leadership is crucial for improving patient care, supporting teams, and advancing the profession. Leadership programs for nurses focus on decision-making, mentorship, and inspiring innovation.
Key Elements of Nursing Leadership:
Mentorship Programs: Guide new nurses toward career growth and success.
Workforce Training: Develop strategies to enhance team efficiency and patient outcomes.
Healthcare Quality Improvement: Lead initiatives to elevate care standards.
Empowering Nurses: Foster confidence and professional autonomy.
Compassionate Care for Elderly Patients
Caring for elderly patients demands specialized nursing skills and a deep sense of empathy. Compassionate care for elderly individuals enhances their quality of life, especially in cases involving dementia, Alzheimer’s, or chronic illnesses.
Tips for Elderly Care:
Prioritize Comfort and Safety: Adapt the environment to meet mobility and sensory needs.
Engage in Meaningful Activities: Encourage hobbies and social interaction.
Monitor Nutrition: Ensure balanced diets tailored to aging bodies.
Provide Emotional Support: Offer companionship and understanding during challenging times.
The Importance of Healthcare Empathy in Nursing
Healthcare empathy bridges the gap between clinical competence and patient trust. By understanding patients’ experiences, nurses can deliver compassionate and effective care.
Building Empathy in Nursing:
Active Reflection: Practice mindfulness to remain present and engaged.
Effective Patient Communication: Use open-ended questions to understand patient concerns.
Empathy Training: Participate in workshops to enhance emotional intelligence.
Professional Development in Nursing
Career advancement in nursing requires a commitment to lifelong learning. Opportunities for growth include continuing education, certifications, and specialized training programs.
Top Development Programs for Nurses:
Nursing Education Programs: Strengthen foundational knowledge.
Nursing Leadership Training: Prepare for supervisory roles.
Healthcare Mentoring: Learn from experienced professionals.
Specialized Certifications: Gain expertise in areas like oncology or critical care.
Nursing Self-Care: Maintaining Personal Well-Being
To provide the best care, nurses must prioritize their own health and well-being. Self-care reduces burnout and ensures sustained effectiveness.
Self-Care Strategies:
Maintain Physical Health: Exercise regularly and eat a balanced diet.
Set Boundaries: Avoid overcommitting to prevent fatigue.
Seek Emotional Support: Join professional networks or counseling groups.
Engage in Relaxation Techniques: Practice yoga, meditation, or hobbies.
Conclusion: Compassionate Care Starts with You
Compassionate care is not just a skill but a mindset that transforms patient outcomes and enriches nursing practice. At NurseSkillsHub.com, we believe in empowering nurses to excel through education, leadership, and empathy. By prioritizing personal and professional growth, nurses can make a lasting impact on their patients’ lives.
Explore more resources and programs at NurseSkillsHub.com to elevate your nursing career and provide exceptional care. Together, let’s build a future where compassion and excellence go hand in hand.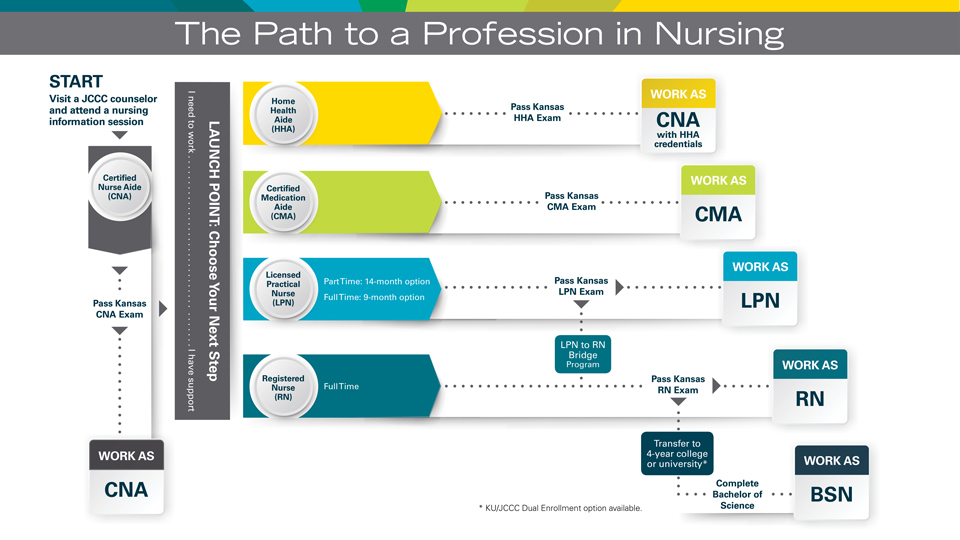
The Role of Compassionate Care in Nursing
Compassionate nursing goes beyond clinical expertise. It involves empathy, active listening, and genuine concern for patients’ physical, emotional, and mental well-being. This approach is especially vital in creating trust, ensuring adherence to treatment plans, and improving patient satisfaction.
Key Benefits of Compassionate Care:
Improved Patient Outcomes: Empathy and kindness encourage cooperation, leading to faster recoveries.
Stronger Nurse Skills Hub-Patient Relationships: Building trust fosters open communication and enhances care delivery.
Increased Patient Satisfaction: Compassion helps patients feel valued, reducing anxiety and stress.
Positive Workplace Culture: A focus on empathy benefits not only patients but also healthcare teams.
Essential Nursing Skills for Quality Patient Care
Quality patient care relies on advanced nursing skills and consistent professional development. Nurses must blend technical expertise with emotional intelligence to provide well-rounded care. The following skills are vital for success:
Clinical Nursing Skills:
Effective Nursing Communication: Ensures clarity in patient interactions and fosters understanding.
Nursing Care Techniques: Includes wound care, IV administration, and pain management in nursing.
Patient Advocacy: Protecting patient rights and ensuring ethical care delivery.
Advanced Care Planning: Helps patients make informed decisions about their healthcare.
Compassionate Nursing Techniques:
Active Listening: Understanding patient concerns and responding empathetically.
Emotional Support for Patients: Addressing fears and offering reassurance during critical moments.
Personalized Care Plans: Tailoring treatments to individual needs, especially for the elderly or chronically ill.
Nursing Education: Building a Foundation for Excellence
Education is the cornerstone of professional nursing development. Continuous learning equips nurses with the tools they need to adapt to evolving healthcare challenges.
Key Areas of Nursing Education:
Nursing Certifications: Programs like Basic Life Support (BLS) and Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support (ACLS) build critical care skills.
Nursing Training Programs: Hands-on training sharpens both technical and soft skills.
Clinical Nursing Education: Enhances decision-making through evidence-based practices.
Healthcare Leadership for Nurses: Prepares professionals for management roles and fosters teamwork.
Patient-Centered Care: Prioritizing Individual Needs
Patient-centered care places the individual at the core of healthcare delivery. This holistic approach ensures that treatment aligns with patient values, preferences, and circumstances.
Strategies for Patient-Centered Nursing:
Care Coordination Skills: Collaborate across teams to provide seamless care.
Cultural Competency: Respect diverse backgrounds and tailor care accordingly.
Patient Advocacy: Champion patient rights while navigating healthcare systems.
Holistic Nursing Care: Address physical, emotional, and psychological needs.
Nursing Leadership: Driving Change in Healthcare
Effective nursing leadership is crucial for improving patient care, supporting teams, and advancing the profession. Leadership programs for nurses focus on decision-making, mentorship, and inspiring innovation.
Key Elements of Nursing Leadership:
Mentorship Programs: Guide new nurses toward career growth and success.
Workforce Training: Develop strategies to enhance team efficiency and patient outcomes.
Healthcare Quality Improvement: Lead initiatives to elevate care standards.
Empowering Nurses: Foster confidence and professional autonomy.
Compassionate Care for Elderly Patients
Caring for elderly patients demands specialized nursing skills and a deep sense of empathy. Compassionate care for elderly individuals enhances their quality of life, especially in cases involving dementia, Alzheimer’s, or chronic illnesses.
Tips for Elderly Care:
Prioritize Comfort and Safety: Adapt the environment to meet mobility and sensory needs.
Engage in Meaningful Activities: Encourage hobbies and social interaction.
Monitor Nutrition: Ensure balanced diets tailored to aging bodies.
Provide Emotional Support: Offer companionship and understanding during challenging times.
The Importance of Healthcare Empathy in Nursing
Healthcare empathy bridges the gap between clinical competence and patient trust. By understanding patients’ experiences, nurses can deliver compassionate and effective care.
Building Empathy in Nursing:
Active Reflection: Practice mindfulness to remain present and engaged.
Effective Patient Communication: Use open-ended questions to understand patient concerns.
Empathy Training: Participate in workshops to enhance emotional intelligence.
Professional Development in Nursing
Career advancement in nursing requires a commitment to lifelong learning. Opportunities for growth include continuing education, certifications, and specialized training programs.
Top Development Programs for Nurses:
Nursing Education Programs: Strengthen foundational knowledge.
Nursing Leadership Training: Prepare for supervisory roles.
Healthcare Mentoring: Learn from experienced professionals.
Specialized Certifications: Gain expertise in areas like oncology or critical care.
Nursing Self-Care: Maintaining Personal Well-Being
To provide the best care, nurses must prioritize their own health and well-being. Self-care reduces burnout and ensures sustained effectiveness.
Self-Care Strategies:
Maintain Physical Health: Exercise regularly and eat a balanced diet.
Set Boundaries: Avoid overcommitting to prevent fatigue.
Seek Emotional Support: Join professional networks or counseling groups.
Engage in Relaxation Techniques: Practice yoga, meditation, or hobbies.
Conclusion: Compassionate Care Starts with You
Compassionate care is not just a skill but a mindset that transforms patient outcomes and enriches nursing practice. At NurseSkillsHub.com, we believe in empowering nurses to excel through education, leadership, and empathy. By prioritizing personal and professional growth, nurses can make a lasting impact on their patients’ lives.
Explore more resources and programs at NurseSkillsHub.com to elevate your nursing career and provide exceptional care. Together, let’s build a future where compassion and excellence go hand in hand.

- 이전글School Uniform Shop Near Me Contact Number Helps You Achieve Your Dreams 25.05.17
- 다음글SlimJaro: A Raw Solvent for Peeling Pounds 25.05.17
댓글목록
등록된 댓글이 없습니다.




















